Rapid MVP Development: How to Ship in Weeks, Not Months
Building an MVP (Minimum Viable Product) in weeks instead of months is possible with the right approach. Here’s the key takeaway: focus on solving one core problem, prioritize essential features, and use modern tools and workflows to save time. This method isn’t about perfection - it’s about delivering a functional product quickly to gather feedback and validate your ideas.
Key Steps to Build an MVP Fast:
- Define a Clear Scope: Focus on one critical problem and exclude unnecessary features. Use frameworks like the MoSCoW method to prioritize.
- Lean Startup Principles: Use the Build-Measure-Learn loop to test assumptions and refine quickly based on user feedback.
- Agile Development: Break the process into short 2-week sprints to maintain focus and deliver results consistently.
- Leverage Modern Tools:
- AI-assisted coding tools (e.g., GitHub Copilot) to speed up development.
- No-code/Low-code platforms (e.g., Bubble, Webflow) for fast prototyping.
- Backend-as-a-Service platforms (e.g., Firebase, Supabase) to handle infrastructure needs.
- Automate Testing and Deployment: Use CI/CD pipelines and AI-powered testing tools to save time and ensure quality.
Why Speed Matters:
- Markets change fast, and delays can lead to missed opportunities.
- Launching quickly allows you to test and refine with real users.
- Investors value execution over ideas - delivering a working MVP in 30 days demonstrates action, not just talk.
By combining lean strategies, agile workflows, and time-saving tools, you can reduce development costs by up to 50% and launch up to 40% faster. The goal? Ship fast, gather feedback, and iterate smarter.
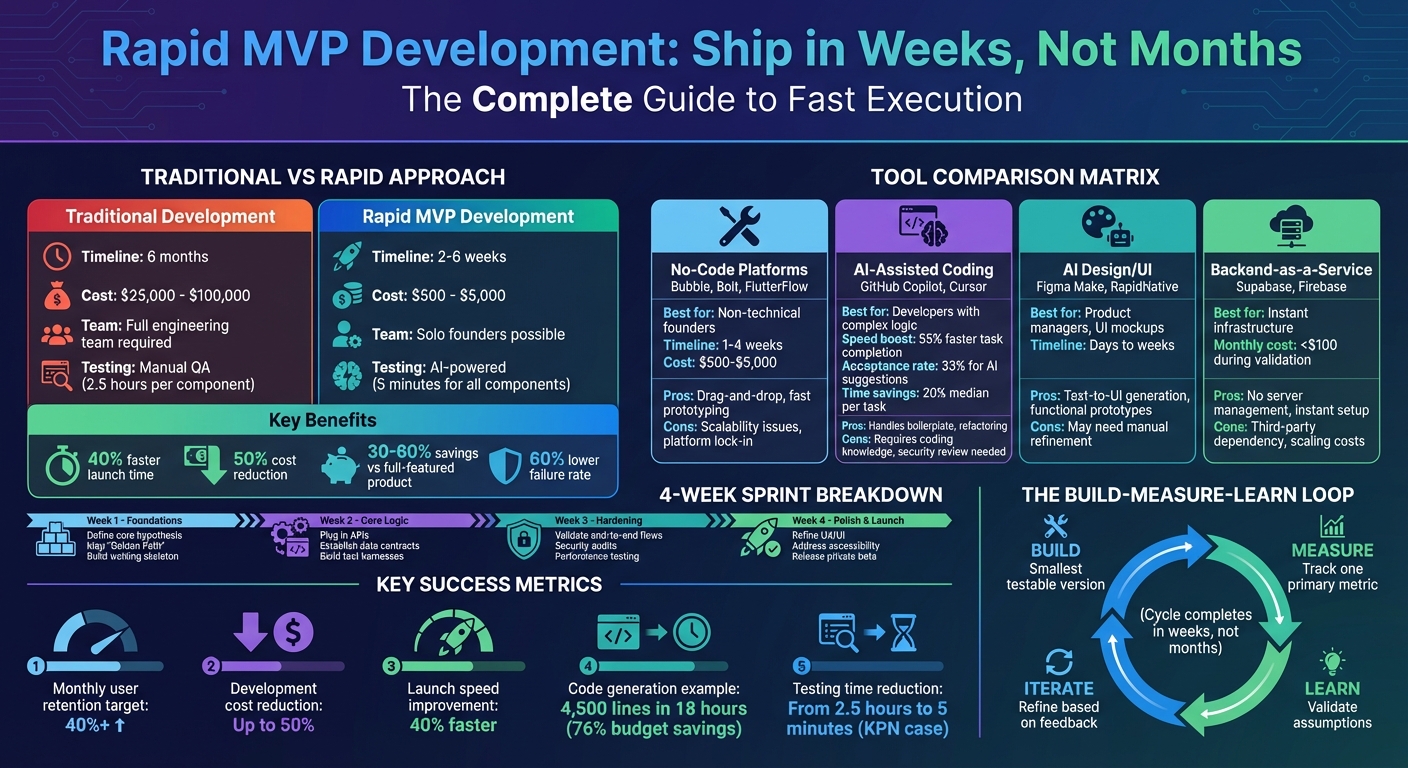
Traditional vs Rapid MVP Development: Cost, Timeline & Tool Comparison
The Fastest Way to Validate Any App Idea (In 48 Hours)
sbb-itb-765bc22
Define Your MVP Scope with Lean Prioritization
One of the hardest parts of building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is deciding what not to include. It’s easy to fall into the trap of adding "just one more feature", which can quickly turn a short, manageable project into a drawn-out, expensive endeavor. The key to avoiding this? Ruthless prioritization. By sticking to an MVP approach, you can cut initial development costs by as much as 30% to 60% compared to creating a full-featured product. That’s a significant amount of money that can be redirected into improving and growing your product later.
Start by crafting a Product Vision Statement - a concise sentence that clearly outlines who your product is for, the problem it addresses, and what success looks like. This statement acts as your guiding light. Next, use user stories to frame the problem: "As a [type of user], I want to [achieve this goal] so that [I get this value]". This approach keeps the focus on the user’s perspective. From there, identify the core "Job-to-be-Done" - the main outcome users are looking for. For example, if you’re designing a scheduling app, the goal isn’t just "manage a calendar." It’s "eliminate the hassle of back-and-forth emails to find meeting times." Once you’ve nailed down the scope, the focus becomes solving one core problem.
Focus on One Core Problem
An MVP should tackle one specific problem exceptionally well, rather than trying to solve an entire set of challenges. This is where the concept of the "Golden Path" comes in - the ideal, straightforward journey a single user persona takes to get value from your product. Forget about edge cases and secondary features for now. For instance, if you’re building an AI-powered document summarizer, the Golden Path might look like this: upload a document → receive a summary. That’s it. No user accounts, no dashboards, no extra bells and whistles. Those can wait until you’ve proven that people actually care about the core functionality.
To stay laser-focused, use the MoSCoW Method to prioritize features: Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, and Won’t-have (for now). Only the "Must-haves" should make it into your MVP. Everything else gets set aside for later. This isn’t about creating a stripped-down version of your dream product - it’s about building the smallest, testable version that demonstrates whether people are interested. An MVP is not the final product; it’s just enough to engage early users and gather feedback for future iterations.
Once you've defined the problem and narrowed the scope, the next step is to validate your ideas quickly and effectively.
Apply Lean Startup Principles
With your MVP scope in place, lean startup principles can help you validate your idea efficiently. These principles revolve around the Build-Measure-Learn loop, a cycle designed to eliminate waste and focus on what’s important. You start by building the smallest version of your idea, then measure how users interact with it, and finally, learn from the results to guide your next steps. The goal is to complete this cycle in weeks - not months. Start by documenting your assumptions: What do you expect the product to achieve? How do you think users will behave? Turning these assumptions into testable hypotheses makes it easier to confirm or disprove your ideas quickly.
Another crucial step is to define one primary metric before development begins. This metric could be anything from "time to complete a task" to "conversion rate" - whatever demonstrates that your product is solving the main problem. Use this metric as a filter: if a feature doesn’t directly support it, leave it out. You can also use AI tools to challenge your assumptions. Present your product concept to an AI and ask for potential flaws or overlooked factors. This kind of testing can help you spot weaknesses early, saving time and resources.
The goal isn’t perfection - it’s to prove that your idea has potential. Once you’ve validated the core concept, you can start building from there.
Use Agile Development and Sprint-Based Workflows
Once you've defined the scope of your MVP, it's crucial to keep the momentum going by adopting agile, sprint-based workflows. Rather than treating your MVP as one massive project that stretches on for months, break it into short, focused cycles. This forces the team to prioritize ruthlessly and consistently deliver tangible results. By working in this way, you avoid scope creep and ensure the team stays laser-focused on delivering a functional product.
The secret lies in timeboxing. As Oleg Tagobitsky, CEO of Re:plain, explains:
"Timeboxing your build into a 4-week sprint doesn't mean cutting corners - it means sharpening focus".
This approach has proven its worth in real-world scenarios. For instance, a fintech startup developed an MVP in just eight weeks using React Native. They concentrated on five essential features, released the product to 100 beta users, and successfully secured $2M in Series A funding. The sprint structure forced them to make tough decisions about what mattered most, and the results spoke volumes.
Next, let's dive into how to structure your development process using effective 2-week sprints.
Structure Development into 2-Week Sprints
Breaking your MVP development into 2-week sprints helps balance speed with quality. Each sprint should focus on delivering a specific functionality that aligns with your "Golden Path" - the most valuable user journey. The first week of a sprint should aim to deliver a "walking skeleton": a basic, functional structure with placeholder endpoints that can be deployed immediately. This allows the team to demo and iterate on something tangible right away, rather than waiting until all the pieces come together.
Here’s how a typical 4-week sprint cycle might look:
| Sprint Phase | Focus Area | Tasks |
|---|---|---|
| Week 1 | Foundations | Define core hypothesis, map "Golden Path", build walking skeleton |
| Week 2 | Core Logic | Plug in APIs, establish data contracts, build test harnesses |
| Week 3 | Hardening | Validate end-to-end flows, conduct security audits, perform performance testing |
| Week 4 | Polish & Launch | Refine UX/UI, address accessibility issues, and release a private beta |
This sprint structure also supports parallel workstreams. By freezing API contracts and data interfaces by the midpoint of the sprint, you prevent frontend developers and testers from being blocked by backend development. For example, the UI team can proceed with building against fixed endpoints while the backend finalizes its logic.
A great example of this approach comes from Thinslices in early 2025. Their team built a functional inventory management MVP in just 72 hours. Using a junior frontend developer and AI tools like Lovable.dev and Bolt.new, they created a tool with role-based logins, stock input, and threshold alerts - all without needing a full backend team.
Build Collaboration and Accountability
For sprints to succeed, structured collaboration is non-negotiable. Speed without coordination leads to chaos, so the sprint model only works if the team stays aligned and accountable. Start with daily demo-driven syncs - quick 15-minute meetings where team members showcase their progress instead of just talking about it. Rather than vague updates like "working on the API", these meetings focus on demonstrating actual API responses and verifying that the UI matches the expected schema. This kind of hands-on alignment catches issues early, saving time and effort later.
Cross-functional collaboration is another cornerstone. From day one, your team should include UI/UX designers, product managers, and engineers working together - not in isolated silos. Assign atomic tasks - small, independently testable pieces of work that can be completed in a day or two. For example, instead of assigning "build the user dashboard", break it into smaller tasks like "create API endpoint for user data", "design dashboard wireframe", "implement dashboard UI", and "write integration tests." Each task should have a clear owner and a well-defined outcome.
Accountability also thrives on automation. Set up CI/CD pipelines from the start so that every code push automatically deploys to a test environment. This eliminates the manual deployment bottleneck and ensures the team always has a current version to test. Use automated code reviews and testing tools to maintain quality without slowing down progress. The goal is to create a system where everyone can see progress, problems are identified quickly, and each team member knows exactly what they need to deliver by the end of the sprint.
Use AI Tools and Automation to Accelerate Development
Incorporating AI tools and automation into your workflow can take agile sprints and lean prioritization to the next level, speeding up your MVP development process. These tools handle time-consuming tasks like writing boilerplate code, setting up test environments, and performing manual bug checks. For instance, developers using GitHub's AI coding assistant reported completing tasks 55% faster, while product managers leveraging generative AI managed to cut product time-to-market by around 5% within a six-month cycle.
AI also opens the door to advanced coding capabilities without the usual overhead. Take the example of MobiDev, which in late 2024 developed a CRM MVP for the startup Treegress. By combining AI-assisted coding with senior engineering oversight, they produced 4,500 lines of production-ready code across five core modules in just 18 hours. This approach saved 76% of the budget compared to the initial 130-hour manual estimate. As OpenTools.ai aptly put it:
"Speed no longer comes from cutting corners - it comes from cutting repetition".
Let’s explore how specific AI tools can simplify coding and testing tasks.
AI-Assisted Code Generation
AI-powered tools like GitHub Copilot, Cursor, and Claude Code are changing the way developers write code by automating repetitive tasks. These tools can handle boilerplate code, refactoring, and even unit tests, freeing developers to focus on the more complex aspects of business logic. Between November and December 2024, ZoomInfo rolled out GitHub Copilot to over 400 developers. The results? A 33% acceptance rate for AI-generated code suggestions, a 72% developer satisfaction score, and a 20% time savings on average across tasks. This allowed 63% of their developers to accomplish more per sprint.
To get the best results, treat AI as a teammate. Break features into smaller, manageable parts and test each one thoroughly before moving forward. Always use version control systems like Git or GitHub to safeguard your work, as AI-generated code can sometimes introduce errors. Providing clear context - such as a well-defined Product Requirements Document (PRD) or a design snippet - can improve the consistency of outputs. While AI can draft solutions, it’s crucial to have experienced developers review the architecture and ensure it meets security standards.
Once the code is generated, automated testing can take efficiency even further.
Automate Testing and Deployment
AI tools excel in testing and deployment, saving significant time in these critical stages. AI-powered testing tools can autonomously execute interaction flows, detect regressions, and generate error logs, cutting down manual QA time. For example, KPN managed to reduce its testing time from 2.5 hours per component to just 5 minutes for all components using AI-driven tools. Solutions like Testim, CodiumAI, and AgentHub automate regression and edge-case testing, catching potential issues before they hit production.
Pair these AI-driven testing tools with automated CI/CD pipelines from the start. Tools like GitHub Actions or GitLab CI ensure that each code push is deployed to a test environment. This setup keeps a current version ready for testing and enables your team to iterate multiple times daily instead of weekly. AI-driven testing and review agents monitor every commit, allowing problems to be identified and resolved almost immediately.
Use No-Code and Low-Code Platforms for Prototyping
No-code and low-code platforms are game-changers for fast prototyping, especially when paired with agile and AI-driven strategies. These tools remove many of the hurdles associated with traditional development, allowing non-technical founders to create prototypes in just 1–4 weeks, compared to the 2–6 months typically needed for custom development. With platforms like Bubble, Webflow, and Bolt, users can drag and drop to build front-end interfaces and databases. For backend automation, tools like Zapier and n8n handle workflows without requiring any coding. The cost savings are just as impressive: no-code MVPs range from $500–$5,000, whereas custom development can cost anywhere from $25K–$100K.
For example, in November 2025, entrepreneur Aaron Veale used Figma Make to create a marketplace app in just a few weeks, enabling small growers to sell directly. This example highlights how these platforms can quickly turn ideas into clickable prototypes - and even production-ready code.
How to Choose the Right Platform
The right platform depends on your technical skills and project needs. If rapid prototyping is your goal, no-code platforms like Bubble are a great fit. For projects requiring custom logic, low-code tools like FlutterFlow might be better. To avoid delays and scope creep, set a strict timeline of three weeks for your project. This approach helps you focus on solving one critical problem at a time. As Michael Seibel, Managing Director at Y Combinator, advises:
"Hold the problem you're solving tightly, hold the customer tightly, hold the solution you're building loosely".
While these platforms are excellent for speed, they do come with some limitations.
Speed vs. Flexibility Tradeoffs
The speed of no-code solutions comes at a cost. These platforms often struggle with advanced features, complex integrations, or highly customized solutions that break away from standard patterns. They’re great for validating ideas, but scaling your product or adding complexity may require extensive refactoring - or even moving to custom development. Additionally, third-party API updates can disrupt key functionalities.
To prepare for these challenges, plan your migration strategy early. Keep your architecture clean and document your workflows to ensure a smooth transition when the time comes. Focus on solving the core problem first and validating market demand before worrying about scalability. During the validation phase, many startups can operate for less than $100 per month using these platforms, making them an affordable way to test ideas before investing in costly custom development.
Build Continuous Validation and Feedback Loops
Shipping quickly won’t help if you’re creating the wrong product. Continuous validation isn’t just a nice-to-have - it’s what separates an MVP that resonates with users from one that wastes time and money.
To stay on track, validate your assumptions regularly with prototypes, feature flags, and incremental releases. This approach keeps development cycles focused and ensures you’re solving a real problem before committing more resources. Plus, this process naturally helps you identify the metrics that truly matter.
Set Clear KPIs for Validation
Start by defining a single, core metric that will validate your MVP. This could be something like time saved, task completion rate, or conversion percentage - whatever best measures the problem you’re addressing. Without a clear focus, you risk gathering data that doesn’t provide actionable insights.
Use tools like Mixpanel or PostHog to track user actions, such as clicks, drop-offs, and hesitation points. Pair this data with short surveys or post-session interviews to understand user behavior better. For example, ZoomInfo monitored GitHub Copilot’s performance with over 400 developers between November and December 2024. They found a 33% acceptance rate for AI suggestions and a 20% median time savings per task.
Make sure your analytics are set up before any tests begin. Tools like Hotjar or FullStory can capture session replays, letting you see exactly where users run into problems. Feature flags, such as those from LaunchDarkly, allow you to test new features with small groups and roll them back instantly if needed.
Conduct User Testing
Testing with just 5–10 target users can uncover major issues. Pay attention to where users hesitate or make mistakes, and focus on refining the "golden path" - the main user flow that delivers your product’s core value.
Initially, ignore edge cases. If users can’t complete the primary task smoothly, nothing else matters. Follow a weekly testing cycle: collect data, identify a key flaw, implement an update, and repeat. This rhythm keeps feedback loops short and ensures you’re addressing real user needs instead of building unnecessary features.
Speed up your analysis with AI tools. These can quickly group themes from support tickets or survey responses, turning what used to take weeks into just a few hours. For instance, KPN used AI-powered tools to reduce component testing time from 2.5 hours to just 5 minutes. The faster you can process feedback, the quicker you can refine and release updates that genuinely improve the user experience.
Tools for Fast MVP Development
When it comes to building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) quickly, choosing the right tools can make all the difference. With lean and agile strategies at the forefront, today’s tools allow even solo founders to achieve what once required an entire engineering team. The trick lies in aligning your toolset with your team’s expertise, the complexity of your MVP, and the flexibility you might need as your product evolves. Let’s dive into some key categories of tools that can speed up MVP development.
No-code platforms like Bubble and Bolt make it possible to validate ideas in just days. These tools are perfect for non-technical founders, offering drag-and-drop functionality to create working web apps without writing a single line of code. However, they come with limitations - such as difficulty handling complex custom logic and potential scalability issues down the line.
AI-assisted coding tools like GitHub Copilot and Cursor act as virtual pair programmers. They handle repetitive tasks like boilerplate code and unit tests, freeing you up to focus on your product’s unique features. For example, between July and December 2023, ZoomInfo used GitHub Copilot with over 400 developers and reported a 33% acceptance rate for AI-generated suggestions, along with a 20% median time savings on tasks.
AI design tools such as Figma Make and RapidNative are game-changers for creating user interfaces. These tools let you describe your vision in plain English, then generate functional UI screens. This means you can move from an idea to a working prototype in just weeks. While they’re fast, they might require manual adjustments to refine edge cases.
Backend-as-a-Service (BaaS) platforms like Supabase and Firebase simplify backend development by providing ready-to-use authentication, databases, and storage solutions. These platforms eliminate the need to manage servers, allowing you to focus on building your product. However, they rely on third-party uptime and can become costly as your app scales. When choosing tools, prioritize your "golden path" - the core user flow that defines your product. If a tool can’t support this critical experience, its speed advantage won’t matter.
Comparison Table: Features and Limitations
Here’s a quick breakdown of these tools, their strengths, and their limitations:
| Tool Category | Example Tools | Best For | Key Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No-Code | Bubble, Bolt, FlutterFlow | Non-technical founders; rapid web apps | Drag-and-drop; built-in workflows; fast prototyping | Scalability issues; platform lock-in; limited custom logic |
| AI-Assisted Coding | GitHub Copilot, Cursor | Developers handling complex logic | Autocompletes code; refactors; exportable code | Requires coding knowledge; needs security review |
| AI Design/UI | Figma Make, RapidNative | Product managers; UI mockups | Text-to-UI generation; functional prototypes | May lack refinement; edge cases need manual fixes |
| Backend/Auth | Supabase, Firebase | Instant infrastructure; data storage | No server management; instant DB and Auth setup | Dependent on third-party uptime; scaling costs |
With AI-powered tools, startups can launch MVPs for as little as $500 to $5,000, compared to the traditional $25,000–$100,000 range. Development timelines also shrink dramatically, with functional MVPs ready in just 2 to 6 weeks instead of six months.
That said, AI tools aren’t perfect. They still require human oversight to ensure code quality and security. AI-generated code can look polished but may contain critical errors or fail to address domain-specific needs. Always review and test thoroughly.
Conclusion: Ship Fast, Iterate Faster
Key Steps for Fast Execution
Creating an MVP in just a few weeks requires sharp focus and the right tools. Prioritizing tasks strategically and sticking to timeboxed sprints can deliver results quickly. AI tools can play a huge role here, taking care of repetitive tasks like code generation, UI mockups, and automated testing. In fact, AI has been shown to help developers finish tasks 55% faster on average. From the start, it's crucial to include analytics and feedback loops. This way, you're making decisions based on real user behavior instead of assumptions. As Eric Ries, author of The Lean Startup, puts it:
"A minimum viable product is a version of a product with just enough features to be usable by early customers who can then provide feedback for future product development".
By combining a lean focus, agile sprints, and the efficiency of AI, teams can lay the groundwork for rapid iterations. Following this approach, teams can launch products 40% faster while cutting development costs by up to 50%. The goal isn’t just to move quickly - it’s to learn faster than your competitors. These steps help transform your initial concept into a product that’s continuously validated by the market.
The Competitive Advantage of Speed
Speed isn’t just about launching quickly - it’s a key strategic advantage. Investors look for traction, and delivering a functional MVP in 30 days shows you can move fast and adapt as needed. The real power lies in iterating faster. Companies that use structured MVP strategies lower their failure rates by 60% because they validate market demand early and adapt based on real-world data.
Post-launch, focus on metrics like monthly user retention (aim for 40% or more) and time-to-value. These numbers can help identify and address friction points before they become costly problems. Use tools like feature flags to test changes with smaller user groups and conduct “Keep, Stop, Start” retrospectives after each sprint to refine your process. The formula is straightforward: launch a product that delivers value at its core, get it in users’ hands, and let their behavior guide your next steps. In fast-moving markets, the team that learns and adapts the quickest has the edge.
FAQs
How do I ensure my MVP solves the right problem?
To ensure your MVP tackles the right problem, begin by defining the core issue from the user's perspective. Talk to potential users and conduct quick market research to uncover their most pressing challenges or unmet needs. Boil this down into a single, actionable problem statement. Then, turn that statement into a measurable hypothesis, like: "Users will save at least 30 minutes per day by automating X." This approach keeps your focus sharp and your objectives clear.
From there, prioritize with precision. Cut out any features that don’t directly address your hypothesis. Adding too much too soon can distract you and delay your launch. Focus solely on the essential feature that solves the main problem. Once your MVP is ready, test it with a small group of users to gather feedback. Use their input to make quick, targeted improvements, ensuring every change ties back to solving the original issue.
By keeping users at the center, testing early, and iterating quickly, you can build an MVP that delivers meaningful results in a matter of weeks.
What are the advantages of using AI tools to speed up MVP development?
AI tools are reshaping how Minimum Viable Products (MVPs) come to life, speeding up the process and making it more efficient. With tools like no-code and low-code platforms, generative code assistants, and AI-powered design systems, teams can quickly create user interfaces, data models, and backend logic. What used to take months can now be done in just weeks. This faster pace not only saves time but also trims costs, allowing smaller teams - or even solo entrepreneurs - to deliver high-quality results without needing a large engineering department.
These tools also make it easier to validate ideas before writing a single line of code. AI-generated market insights, user personas, and mock-ups help confirm whether there’s real demand for your product. This approach significantly reduces the risk of building something the market doesn’t need. Once your MVP goes live, AI tools step in again with automated analytics and feedback, helping you refine features and improve the product based on how users actually interact with it.
Perhaps the most game-changing aspect is how accessible MVP creation has become. With natural-language interfaces, even founders without technical expertise can describe their vision and generate functional prototypes. This frees up time to focus on strategy and launch planning. By combining speed, cost savings, and smarter validation, AI tools are revolutionizing the way MVPs are developed.
How do no-code and low-code platforms impact the scalability of an MVP?
No-code and low-code platforms are fantastic for getting an MVP off the ground quickly. These tools let teams build functional products in a matter of weeks by leveraging drag-and-drop components, pre-built APIs, and visual workflows. The best part? They cut out the need for heavy coding, making them a budget-friendly way to test ideas early on.
That said, these platforms aren’t without their challenges, especially when it comes to scaling. As your product grows, you might run into hurdles like limited customization options, platform-specific restrictions, or struggles with managing higher traffic loads. At some point, transitioning to custom development or a more flexible infrastructure could become necessary to handle the demands of a more complex product.
No-code and low-code tools are excellent for speed and early-stage validation, but it’s crucial to think ahead about scalability to ensure your product can keep up as it evolves.
